
NMMO is an open-source research platform that simulates populations of agents in virtual worlds. We challenge you to train agents that generalize to tasks, opponents, and maps never seen during training. Our objective is to spur research on increasingly general and cognitively realistic environments.
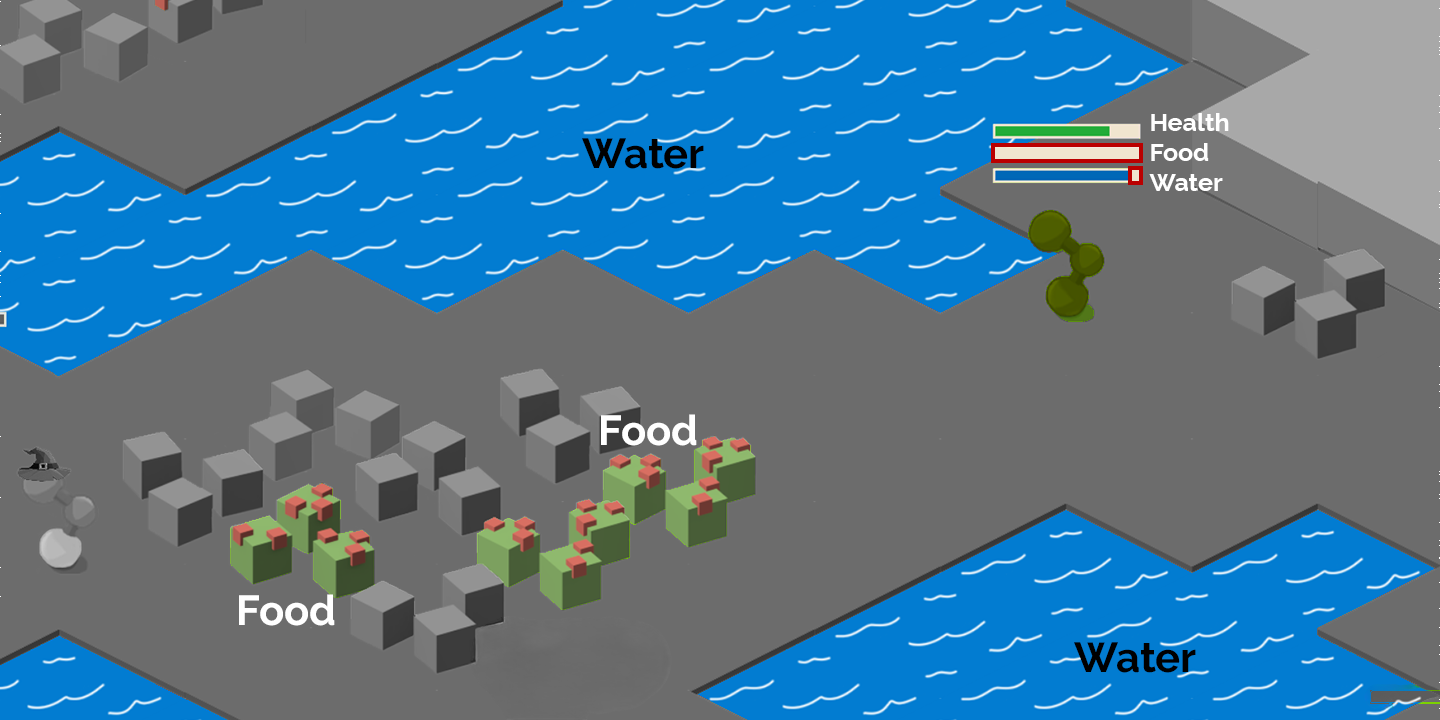
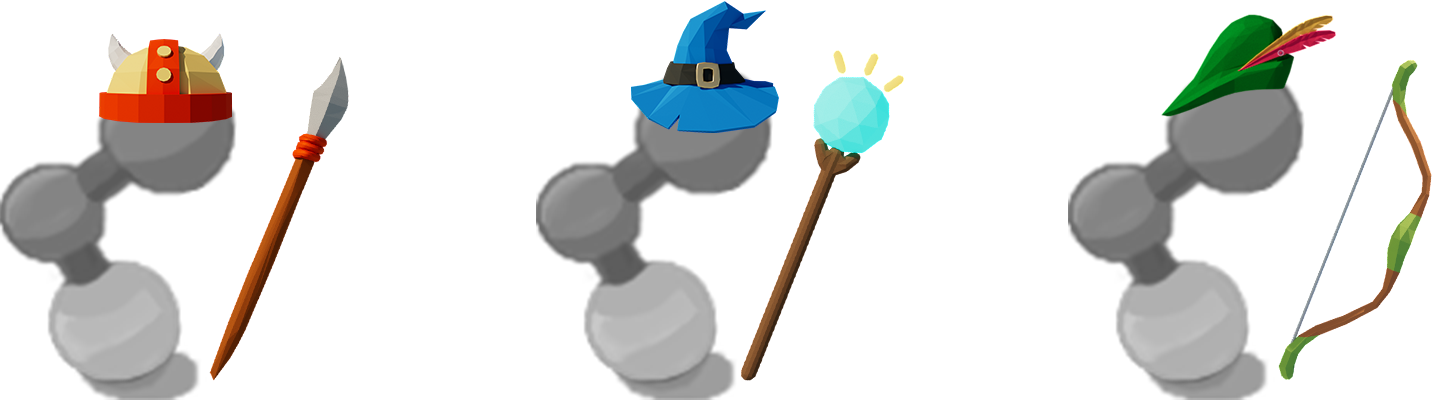
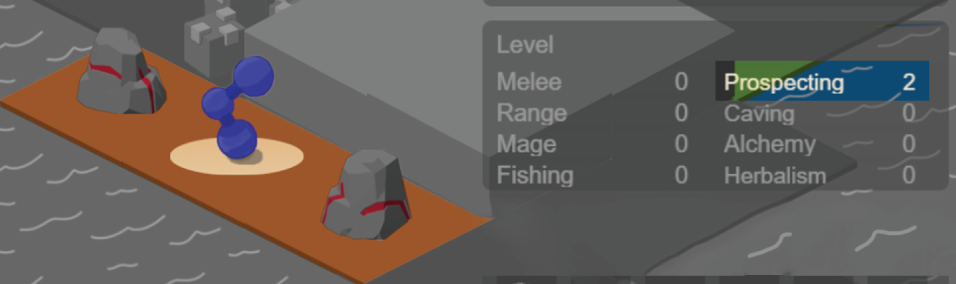
Your Agents must collect food and water to survive. Each Agent has 8 individual professions to help them collect resources. Agents can level up their skills in each profession. Resources can be used to create consumable items that restore food, water and heath as well as to create ammunition that increases damage in combat. Higher level resources create better consumables and ammunition. Agents can also trade items on a global market. Agents may aquire armor to protect themselves in combat and weapons to increase their damage output. Agents can attack each other using one of three styles: Melee, Range, and Magic. The world is populated by NPCs that can be defeated to obtain items and increase power.
Harvest resources with various uses

Forage for food and water to maintain your health
Fight other agents and NPCs with Melee, Range, and Magic

Interact with Non-Playable Characters of varying friendliness

Train combat and profession skills to access higher level items and equipment
Acquire consumables and and ammunition through professions

Increase offensive and defensive capabilities with weapons and armor

Trade items and equipment with other agents on a global market

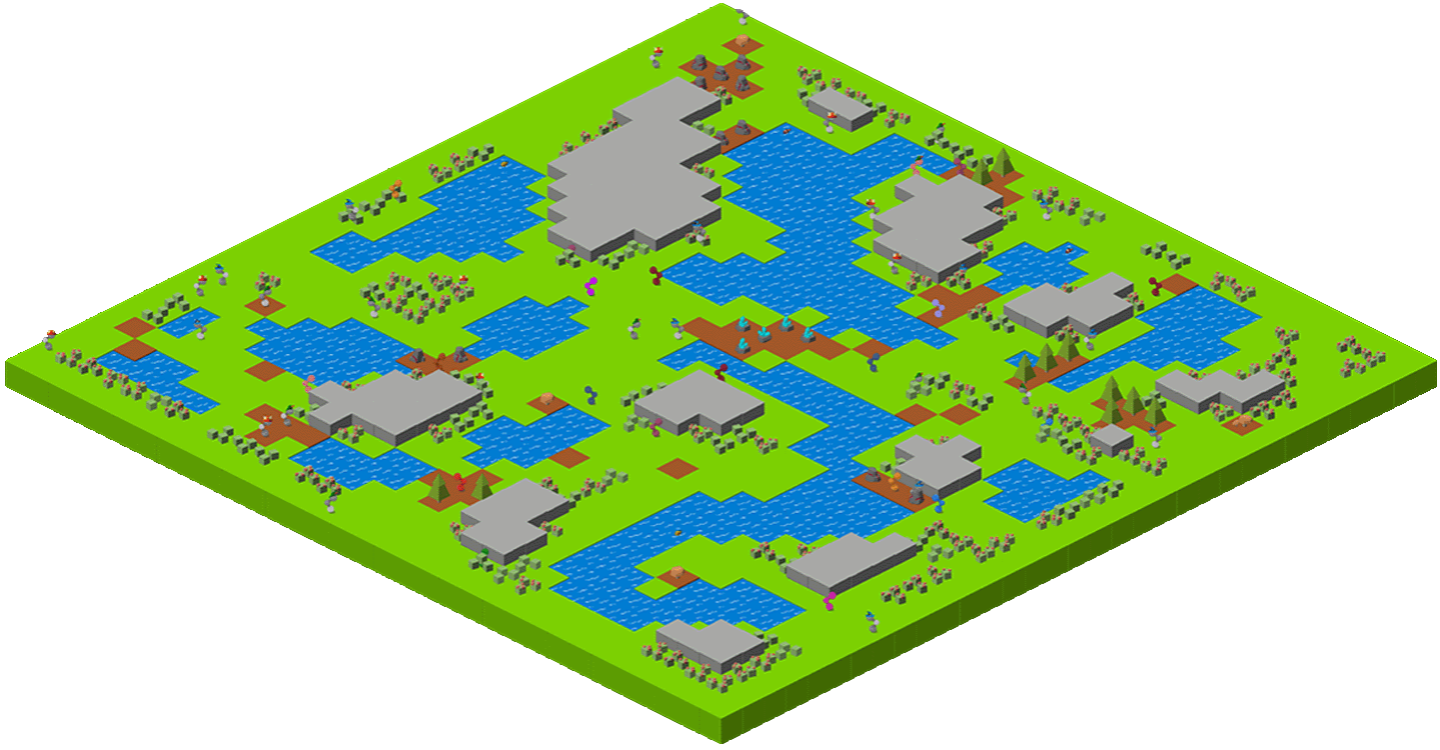
Navigate procedurally generated maps
Contributors
Joseph Suarez: Creator and lead developer of Neural MMO.
- CarperAI team for NMMO 2.0:
Kyoung Whan Choe: Rewrite of Neural MMO game code and logging for 2.0, contributions to the RL baseline and task system
David Bloomin: Rewrite of the engine for 2.0, port and development of the RL baseline
Hao Xiang Li: Neural MMO 2.0 task system
Nikhil Pinnaparaju: Co-developer of the ELM curriculum baseline
Nishaanth Kanna: Co-developer of the ELM curriculum baseline
Daniel Scott: Co-developer of the ELM curriculum baseline
Ryan Sullivan: Integration with Syllabus for the curriculum learning baseline
Rose S. Shuman: Technical writing for this documentation site and for the competition
Lucas de Alcântara: Design and artwork for the 2.0 client
Herbie Bradley: Supervision of the curriculum generation baseline with OpenELM
Louis Castricato: Co-founder and team lead of Carper AI; supervisor of Carper AI development efforts
- Parametrix.ai Team. Competition orchestrators and creators of the 2.0 web client.
Mudou Liu: Machine learning researcher, Parametrix.ai
Kirsty You: Product manager, Parametrix.ai
Yuhao Jiang: Machine learning researcher, Parametrix.ai
Qimai Li: Senior machine learning researcher, Paramerix.ai
Jiaxin Chen: Senior machine learning researcher. Co-organizer of 3rd and 4th Neural MMO Challenge
Xiaolong Zhu: Senior R&D Director, Paramerix.ai
Nick Jenkins: Layout for design for the competition poster. Adversary.design.
Sara Earle: Created 2D icons for items in NMMO 2.0. Hire her on UpWork if you like what you see here.
- Previous open source contributors, listed by time since latest contribution. Discord handle have been used for individuals who have not granted explicit permission to display their real names:
Thomas Cloarec: Developed the dynamic programming backend for scripted baseline agents
Jack Garbus: Major contributions to the logging framework, feedback on the documentation and tutorials
@tdimeola: Feedback on the documentation and tutorials
@cehinson: Mac build of the Unity3D client
Yilun Du: Assisted with experiments for 1.0 at OpenAI
BibTex Citation
@inproceedings{nmmo2_neurips,
author = {Suarez, Joseph and Choe, Kyoung Whan and Bloomin, David and Li, Hao Xiang and Pinnaparaju, Nikhil and Kanna, Nishaanth and Scott, Daniel and Sullivan, Ryan and Shuman, Rose and de Alcantara, Lucas and Bradley, Herbie and Yu, Chenghui and Jiang, Yuhao and Li, Qimai and Chen, Jiaxin and Zhu, Xiaolong and Castricato, Louis, and Isola, Phillip},
booktitle = {Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
editor = {A. Oh and T. Neumann and A. Globerson and K. Saenko and M. Hardt and S. Levine},
pages = {50094--50104},
publisher = {Curran Associates, Inc.},
title = {Neural MMO 2.0: A Massively Multi-task Addition to Massively Multi-agent Learning},
url = {https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2023/file/9ca22870ae0ba55ee50ce3e2d269e5de-Paper-Datasets_and_Benchmarks.pdf},
volume = {36},
year = {2023}
}
@inproceedings{nmmo_neurips,
author = {Suarez, Joseph and Du, Yilun and Zhu, Clare and Mordatch, Igor and Isola, Phillip},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems Track on Datasets and Benchmarks},
editor = {J. Vanschoren and S. Yeung},
pages = {},
title = {The Neural MMO Platform for Massively Multiagent Research},
url = {https://datasets-benchmarks-proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2021/file/44f683a84163b3523afe57c2e008bc8c-Paper-round1.pdf},
volume = {1},
year = {2021}
}
 Installation#
Installation#
- Docker container including Neural MMO and GPU-accelerated baselines. Guarantees correct dependencies and environment setup. We recommended the following setup for local containerized development:
Install Docker Hub, VSCode, and the VSCode dev containers plugin.
Clone PufferTank on Linux/MacOS/WSL
VSCode: F1 -> “Remote-Containers: Open Folder in Container” -> Select PufferTank folder
git clone https://github.com/pufferai/puffertank
Official support for Ubuntu 20.04/22.04, WSL, and MacOS
# Quotes for mac compatibility.
pip install "nmmo"
# Clone baselines repository
git clone https://github.com/neuralmmo/baselines
Only recommended for developers of Neural MMO who can’t run PufferTank.
mkdir neural-mmo && cd neural-mmo
git clone https://github.com/neuralmmo/environment
git clone https://github.com/neuralmmo/baselines
cd environment && pip install -e .[all]
# If you want a local copy of the client.
# WSL users should run this part on Windows
# Download Cocos2d to open
git clone https://github.com/neuralmmo/client
Neural MMO provides a standard PettingZoo interface:
import nmmo
env = nmmo.Env()
obs = env.reset()
for step in range(10):
actions = {a: env.action_space(a).sample() for a in env.agents}
obs, rewards, dones, infos = env.step(actions)
 2023 Competition#
2023 Competition#
Successfully complete the most tasks to win! At stake are $20,000 in prizes sponsored by Puffer AI. Now completed. Hosted on [AICrowd] October 20 - December 15, 2023. Cowon by NetEase Games OPD (Jianming Gao, Yunkun Li, Zhaohao Liang, Jin Gao - team name Takeru) and Yao Feng (participant name yaofeng1998). Third place awarded to Saidinesh Pola. Fourth and fifth jointly shared by Zhang Kun (mori) and Yonghui Zhu (Jimyhzhu). Winning submissions now open sourced in the Neural MMO baselines repository. Evaluation servers are no longer enabled, but you may use the setup instructions below for primary research on Neural MMO, evaluating locally.
Neural MMO (NMMO) has three tracks to compete and win. In all tracks, the objective is for your 8 agents to accomplish more tasks than 120 other opponent. Your submission will be evaluated over thousands of rounds with increasingly difficult tasks. Lobbies are made by a matchmaking algorithm that selects 16 teams of similar skill level. The RL and curriculum tracks are compute-limited: we will verify that winners’ solutions can be trained in 8 A100 hours with 12 cores.
- Objective:
Train teams of agents using Reinforcement Learning (RL) to complete tasks. The RL track provides a fixed baseline curriculum of tasks for training. Customize the RL algorithm, model, and reward structure to maximize task completion.
To get started:
NMMO Baseline Repository:
├── reinforcement_learning
│ ├── config.py
│ └── policy.py --> Your policy goes here
├── requirements.txt
└── train.py --> Train your policy here
# Test that training runs
python train.py --local-mode true
# Run training. This is very memory intensive!
# You can change --num-envs and --rollout-batch-size to adjust memory usage
# Also check out --device and --seed
# The checkpoints are saved under --runs_dir with --run_name
python train.py --run-name <YOUR_RUN_NAME> --device <YOUR_DEVICE> --seed <YOUR_NUMBER> --num-envs 1 --rollout-batch-size 2**14
# Evaluate checkpoints. After training, copy your checkpoints into policies
# The below command will compare your checkpoints against the baseline policy
python evaluate.py -p policies
# To generate a replay, create a directory with your checkpoints then run
python evaluate.py -p <YOUR_DIR> -r
- Overview:
This competition track is ideal to showcase your RL skills. Successful entrants develop agents that thrive in a massively multiagent environment with potential adversaries, successfully completing assigned tasks.
Your RL track objective is to implement an agent policy for that dictates their performance in a new environment. Each game starts with your team receiving a randomly generated task. If the team completes the task, it earns a point. Your team will play thousands of games, each with a new assigned task to complete. The team with the highest score wins the competition.
- You have control over the:
RL algorithm
Environment rewards signal
Observation featurization
Neural network architecture
- Baseline:
The baseline is designed for ease of use and modification. We recommend using it as a starting point for your submissions. It provides task presentation and sampling, treated as constants.
All RL agents train using the same baseline task curriculum. Hybrid methods are allowed, but traditional scripting alone is unlikely to be effective because of the new task-oriented focus.
Neural MMO provides a baseline repository that includes a fixed curriculum of procedurally generated tasks, a single-file CleanRL PPO implementation, PufferLib integration for streamlined training, and WandB for logging and visualization.
- Objective:
No RL experience, no problem! Design your own unique and useful curricula for training agent teams on tasks. A curriculum is a structured set of tasks presented to the RL algorithm intelligently that maximizes its learning.
Once trained on your curriculum, your RL policy will navigate the NMMO environment and complete tasks. Using Python, design the: - Task generator - Task sampler - Reward
- Overview:
The Curriculum track offers a platform for programmers to engage and compete, regardless of AI expertise. All submitted curricula will be applied to a common baseline RL policy, controlling a team of agents. Your objective is to devise a curriculum that enhances learning, leading to improved agent performance on previously unseen tasks. You will receive performance metrics to assess the efficacy of your curriculum and refine your training approach.
- Baseline:
The baseline provides the reinforcement learning algorithm, observation featurization, and neural network architecture. These remain consistent across all teams.
The baseline package for this track includes a fixed curriculum of tasks and integration with OpenELM. While encouraging the utilization of ELM (Evolution through Large Model) for advanced users and researchers, we also furnish a code generation model in conjunction with the baselines.
Getting Started with Manual Curriculum Generation Tutorial
This tutorial will guide you through the process of manually creating a curriculum for training agents. The provided code demonstrates the steps required to define training tasks, evaluate them, generate embeddings, and train agents using the defined curriculum. You can see the full working code at https://github.com/CarperAI/nmmo-baselines/blob/release/curriculum_generation/curriculum_tutorial.py
Step 1: Define Your Curriculum
In this step, you’ll define the evaluation functions and training tasks that your agents will learn from. You can use pre-built evaluation functions or create your own. The tasks are specified using the TaskSpec class.
from nmmo.task.base_predicates import CountEvent, InventorySpaceGE, TickGE, norm
from nmmo.task.task_spec import TaskSpec, check_task_spec
# Use pre-built eval functions and TaskSpec class to define each training task
curriculum = [] # is a list of TaskSpec
# Define tasks based on pre-built evaluation functions
essential_events = [ # See nmmo.lib.log, EventCode for the full list
"GO_FARTHEST",
"EAT_FOOD",
"DRINK_WATER",
"SCORE_HIT",
"HARVEST_ITEM",
"LEVEL_UP",
]
for event_code in essential_events:
curriculum.append(
TaskSpec(
eval_fn=CountEvent, # Use a pre-built eval function
eval_fn_kwargs={"event": event_code, "N": 10}, # Arguments for CountEvent
)
)
# Define custom evaluation functions
def PracticeEating(gs, subject):
# Your custom evaluation logic like below
num_eat = len(subject.event.EAT_FOOD)
progress = num_eat * 0.06
if num_eat >= 1:
progress += 0.1
if num_eat >= 3:
progress += 0.3
return norm(progress) # Normalizing the value. See norm() at nmmo.task.base_predicates
curriculum.append(TaskSpec(eval_fn=PracticeEating, eval_fn_kwargs={}))
# Define tasks using a combination of pre-built and custom evaluation functions
def PracticeInventoryManagement(gs, subject, space, num_tick):
return norm(InventorySpaceGE(gs, subject, space) * TickGE(gs, subject, num_tick))
for space in [2, 4, 8]:
curriculum.append(
TaskSpec(
eval_fn=PracticeInventoryManagement,
eval_fn_kwargs={"space": space, "num_tick": 500},
)
)
Step 2: Validate Your Curriculum
It’s essential to check if the defined training tasks are valid in Neural MMO. Invalid tasks can cause training crashes. To validate tasks, run the following code:
from nmmo.task.task_spec import check_task_spec
# Check if the task specs are valid in the environment
results = check_task_spec(curriculum)
num_error = 0
for result in results:
if result["runnable"] is False:
print("ERROR: ", result["spec_name"])
num_error += 1
assert num_error == 0, "Invalid task specs will crash training. Please fix them."
print("All training tasks are valid.")
Also, the tasks must be picklable with dill. To check it, use the following code:
import dill
# Save the task specs to a picklable file
with open(“tmp_curriculum.pkl”, "wb") as f:
dill.dump(curriculum, f)
print("All training task are picklable.")
Step 3: Generate Task Embeddings
The task-conditioned RL needs task embeddings. Use the TaskEncoder class to generate embeddings for the training tasks:
from task_encoder import TaskEncoder
LLM_CHECKPOINT = "Salesforce/codegen25-7b-instruct"
CURRICULUM_FILE_PATH = "custom_curriculum_with_embedding.pkl"
# You need to provide the curriculum file as a module to the task encoder
with TaskEncoder(LLM_CHECKPOINT, curriculum_tutorial) as task_encoder:
task_encoder.get_task_embedding(curriculum_tutorial.curriculum, save_to_file=CURRICULUM_FILE_PATH)
print("Done.")
Step 4: Train Agents with Your Curriculum
Now that you have defined the curriculum and generated embeddings, you can proceed to train your agents using the curriculum. This step is basically the same as the RL track:
from reinforcement_learning import config
from train import setup_env
args = config.create_config(config.Config)
# Provide your curriculum file to the training env
args.tasks_path = CURRICULUM_FILE_PATH
# Additional setup if needed
local_mode = True
if local_mode:
args.num_envs = 1
args.num_buffers = 1
args.use_serial_vecenv = True
args.rollout_batch_size = 2**14
# Set up the agent training environment
trainer = setup_env(args)
# Train agents using the curriculum
while not trainer.done_training():
_, _, infos = trainer.evaluate()
# Training task stats are available in infos
if len(infos) > 0:
# Display training task statistics
# ...
# Train the agents
trainer.train(
update_epochs=args.ppo_update_epochs,
bptt_horizon=args.bptt_horizon,
batch_rows=args.ppo_training_batch_size // args.bptt_horizon,
)
Congratulations! You have successfully created a manual curriculum, generated embeddings, and trained agents using the defined tasks. Now, you can start create a curriculum that can win the competition.
Combine RL and curriculum approaches. Entrants provide their own compute to win via any way possible - just don’t hack our servers!
Deploy both RL and Curriculum approaches to create the ultimate 8 Agent team policy. All methods are open and no constraints on (self-provided) compute. Only restrictions are: no unauthorized modifications of the game or other submissions.
If you are here, you know how to get started. Use any of the above baselines or build your own from scratch. This is the only track that does not strictly require winners to open-source their code. However, we strongly encourage you to do so.
NOTE: We have starter code for this but currently don’t have a way to evaluate on our machines. Come chat with us in Discord, as we should be able to verify submissions manually. This starter kit was added based on community interest in LLM agents and was not part of the original proposal, but we will work on adding some sort of bounty or prize specifically for this category.
The curriculum track includes a 7B parameter codegen model (Salesforce/codegen25-7b-instruct) for generating tasks and task embeddings. As part of the No Holds Barred track, you can also use LLMs to generate scripted policies. This uses a hack of Neural MMO’s internal state API to extract data in a human readable format. Example code with gpt 3.5 is provided in a separate folder:
NMMO Baselines Repository:
├── llm-agent
│ ├── 3b_generate_agent.py
│ ├── __pycache__
│ ├── generated_agent.py --> Scripted agent generated by LLM
│ ├── gpt_generate_agent.py --> Generate agent with GPT
│ ├── gpt_summarize_documentation.py --> Summarize NMMO docs with GPT
│ ├── play_game.py --> Play a game with the generated agent
│ ├── prompt_documentation.txt --> Prompt for summarizing NMMO docs
│ ├── prompt_documentation_summary.txt --> Summarized NMMO docs
│ ├── prompt_example_code.py --> Example code from the scripted API
│ ├── prompt_generate_agent.txt --> Prompt for generating a scripted agent
│ ├── prompt_summarize_documentation.txt --> Prompt for summarizing NMMO docs
│ └── scripted -> Symlink to scripted baseline policies
└── requirements.txt
In order to run the generation code with GPT, include your OpenAI credentials in the environment variables OPENAI_ORGANIZATION and OPENAI_API_KEY.
python gpt_generate_agent.py
python play_game.py
Getting GPT 3.5 to output meaningful programs will take some work. We were only able to get the sample generated agent to work with GPT 4.

